Articles
Encrypted Mosquitto broker in Kubernetes

Mosquitto can usually be installed on an Ubuntu server fairly easily using the APT package manager. By Default, the broker handles unencrypted MQTT connections but it can be configured to use SSL certificates obtained, for example, using Certbot and thus enable MQTTs connections. This configuration is usually achieved by editing the Mosquitto configuration file in /etc/mosquitto so as to point to certificates obtained independently. However, when deploying Mosquitto to Kubernetes, one would prefer not to edit configuration files manually after install. Moreover, in Kubernetes, one can use Cert-manager to obtain SSL certificates. Thus, this article presents an efficient method to deploy a secure MQTTs broker in Kubernetes.
"Resizing" a PVC and its PV in Microk8s
With the storage addon enabled, microk8s can automatically provision a PV when a PVC is created. The size of the PV is set according to that of the PVC. However, PVCs cannot be resized after creation. The PVC could be deleted and recreated with a larger size but this would result in the deletion of the PV and, by extension, all the data stored so far in it. This article presents a workaround to resize a PVC and its corresponding PV without any loss of data.
Multi-user MQTT platform
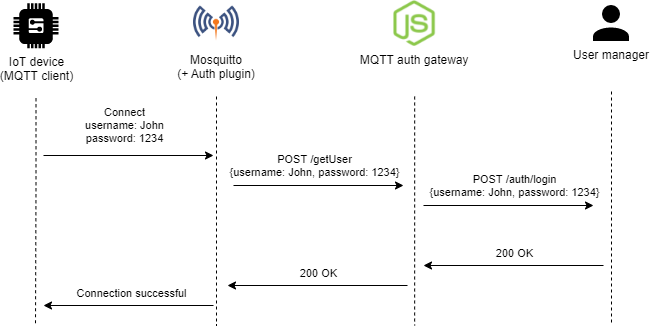
Mosquitto is usually the first candidate to come to mind when looking for an MQTT broker. However, by default, Mosquitto manages users using a password file. This makes it difficult to easily add or remove users, especially when the broker is deployed in Kubernetes.
MongoDB K8s manifest
Here's a simple manifest to deploy MongoDB with data persistence in microk8s:
Cert-manager Certificate Issuer
With cert-manager installed, SSL certificates can be automatically obtained for Ingresses deployed in a Kubernetes cluster. To achieve this, one must deploy the appropriate ClusterIssuers to the cluster. Here are example manifests to do so.
K8s NGINX Deployment for Ingress test
An NGINX container can be quite useful to test whether one's Kubernetes setup is working. Here is one example manifest file that deploys such container with an appropriate service and ingress.
Deploy a Neo4J instance in Kubernetes
Using this manifest, a Neo4J instance can be deployed in a Kubernetes cluster
Deploying a TensorFlow model on a Jetson Nano using TensorFlow serving and K3s
The Nvidia Jetson Nano constitutes a low cost platform for AI applications, ideal for edge computing.However, due to the architecture of its CPU, deploying applications to the SBC can be challenging. In this guide, we'll install and configure K3s, a lightweight kubernetes distribution made specifically for edge devices. Once done we'll build and deploy an TensorFlow model in the K3s cluster.
Node.js DevOps example
In this article, we’ll build a simple Node.js application that uses Express to respond to HTTP requests. In order to deploy this application to production, we’ll also configure a GitLab CI/CD pipeline so as to dockerize it and deploy its container to a Kubernetes cluster.
GitLab CI Microk8s integration
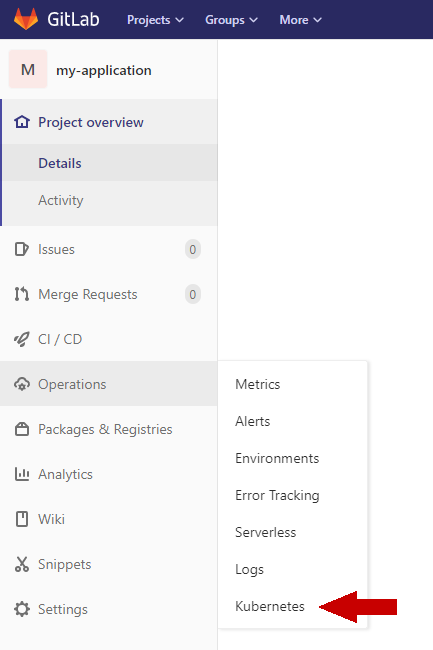
GitLab provides Kubernetes integration out of the box, which means that GitLab CI/CD Pipelines can be used to deploy applications in Kubernetes easily. This guide presents how to integrate a Kubernetes cluster in a GitLab Project and follows Gitlab documentation. For this particular case, the cluster will be that of a Microk8s Kubernetes distribution.